What does a dental nurse do
Dental nurses work alongside dentists and other dental professionals to provide a high standard of care to patients. The specific duties of a dental nurse can vary depending on the dental practice they work in, but some common tasks include:
Preparing the dental surgery for patients: This involves setting up the necessary equipment and materials that will be used during the patient’s appointment.
Assisting the dentist during procedures: Dental nurses will support the dentist by passing them instruments and materials, suctioning, and using equipment such as dental drills.
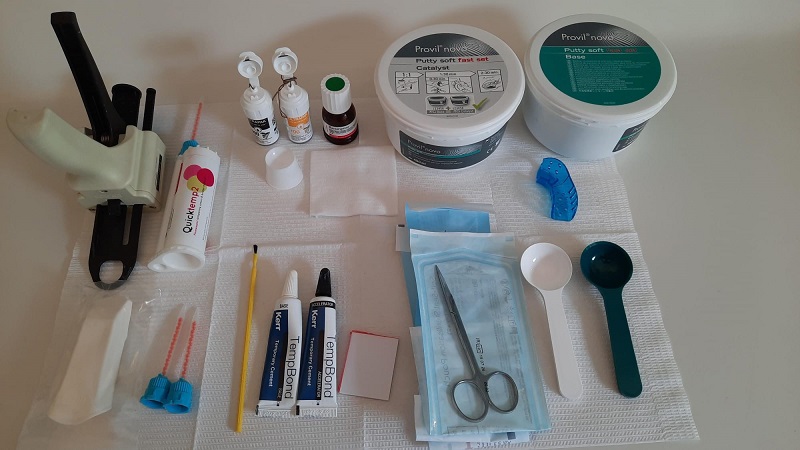
Mixing materials: Dental nurses may be required to mix materials such as dental cement or impression materials.
Taking dental impressions: Dental nurses can take impressions of patients’ teeth and gums using impression materials.
Providing patient care: This includes reassuring and calming anxious patients, answering their questions, and providing aftercare advice.
Maintaining equipment and materials: Dental nurses will clean and sterilize instruments, maintain dental equipment, and order and stock dental materials.
Taking and processing dental radiographs: Dental nurses can take and process dental radiographs (X-rays) under the direction of a dentist.
Administrative tasks: Dental nurses may also be required to undertake administrative tasks such as booking appointments, handling patient records, and processing payments.
How does a dental nurse learn all of these things?
Dental nurses can learn through a combination of formal education and practical training. To become a dental nurse in the UK, individuals must complete a course in dental nursing that is recognized by the General Dental Council (GDC). These courses can be taken at colleges or universities, and they provide learners with a theoretical foundation in dental nursing, including dental anatomy and physiology, radiography, infection control, and patient care. Have a look at the link to our course to see more information on becoming a qualified dental nurse
In addition to formal education, dental nurses also gain practical training through supervised clinical practice in a dental setting. This can involve working in a dental practice, hospital, or community dental service, where they will be supervised by a registered dental professional, such as a dentist or dental hygienist. During this time, they will gain practical experience in supporting dental procedures, providing patient care, and managing dental materials and equipment.
Dental nurses may also undertake further training and professional development throughout their careers to stay up-to-date with the latest developments in dental care and technology. This can include courses in dental hygiene or dental therapy, which can enable dental nurses to take on more advanced roles in the dental team.
See our blog on career progression for dental nurses.
In summary, dental nurses play a vital role in supporting dental professionals and providing high-quality dental care to patients.
What practical training will a dental nurse have to do
As part of their practical training, dental nurses will work under the supervision of a registered dental professional, such as a dentist, dental hygienist or dental therapist. The practical training will involve gaining hands-on experience in the following areas:
- Setting up and preparing the surgery for dental procedures
- Sterilizing and maintaining dental equipment and materials
- Taking and processing dental radiographs (X-rays)
- Assisting the dentist or dental hygienist during dental procedures
- Providing patient care, including reassuring and calming anxious patients, answering their questions, and providing aftercare advice
- Recording patient information and maintaining dental records
- Handling and disposing of clinical waste safely and appropriately
- Managing the patient’s appointment system and booking follow-up appointments
The practical training will also involve learning about the legal and ethical responsibilities of a dental nurse and the importance of maintaining high standards of hygiene and infection control in the dental practice.
The amount of practical training a dental nurse will receive can vary depending on the dental practice they work in, but most courses require a minimum of 750 hours of supervised clinical practice in a dental setting to be completed before the learner can become a registered dental nurse with the General Dental Council (GDC).